 A group of animals that can breed and produce fertile offspring is one of the definitions of a species.
A group of animals that can breed and produce fertile offspring is one of the definitions of a species.
This means that the biological mechanisms of fertility and infertility are of interest not only to evolutionary biologists, but also to clinicians and of course to the wider public. At the Institute of Molecular Genetics in Prague, 教授. Jiri Forejt is studying what controls fertility in the hybrid offspring produced by the mating of mouse sub-species. He wanted to know why some male mice were infertile – he knew that genes in one particular genome region were important, but not how those genes influenced the expression of the rest of the genome.
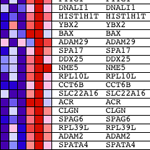
This is where I was recruited into the team, to help with identifying the classes of genes disrupted in mice with reduced fertility. Scientists in his group had produced Affymetrix gene expression results from the testes of fertile, sub-fertile and infertile mice and I analysed these data genome-wide for differentially-expressed transcripts. Using the Broad Institute’s marvellous GSEA tool, I assessed the statistical evidence that specific Gene Ontology terms and pathways were over-represented and also whether differential genes were localised to particular genome regions. This analysis uncovered evidence that specific, functionally related sets of genes were over-represented in the expression data and helped to develop novel hypotheses about the causes of reduced fertility.

一 評論
The paper describing this project was published in PNAS online: “Mechanistic basis of infertility of mouse intersubspecific hybrids” http://buff.ly/10EdYeb